Solar on Grid
What is an On-Grid Solar System?
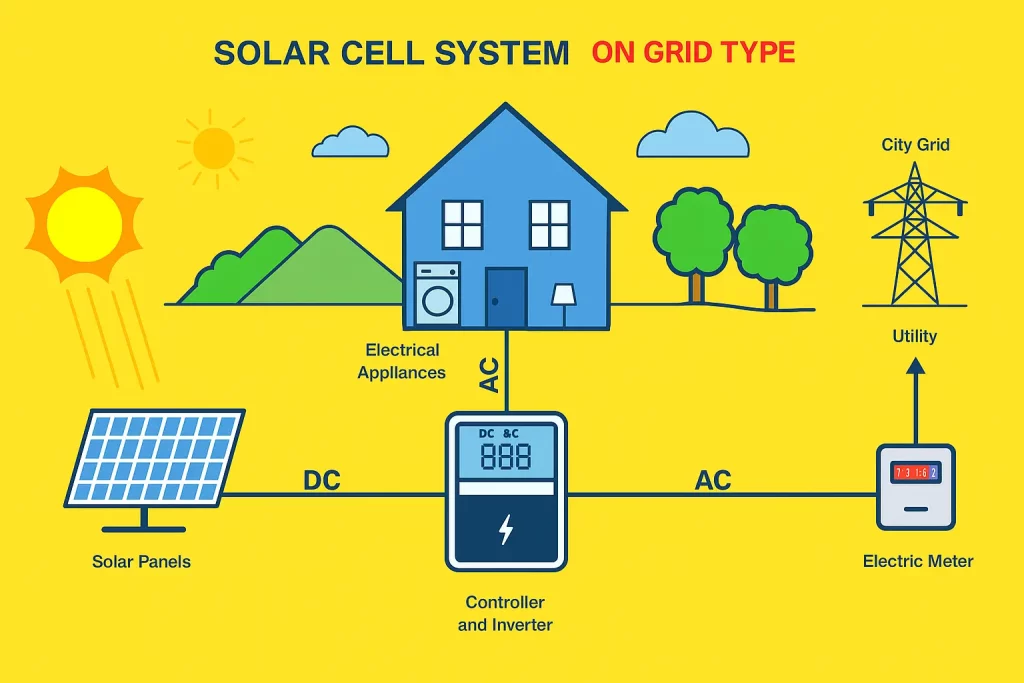
An on-grid (grid-tied) solar system is connected to both your home and the electricity grid. It uses sunlight to generate power during the day, and when needed, pulls electricity from the grid—especially at night or during low solar production.
Essential Components of On-Grid System:
Solar Panels (Mono/Polycrystalline)
Grid-Tied Inverter
Net Meter
Mounting Structure
Protection Devices (MCBs, SPD, etc.)
When it comes to categorization, an on-grid solar power system installed for smaller applications like an individual home has different capacities: 2 kW, 3 KW, 5KW, 10 KW, and so on.
An average Indian household with a monthly electricity bill of ₹1500 to ₹3000 has a requirement of 2 to 3 kW only. For those consuming 0-150 units per month, a subsidy ranging from ₹30,000 to ₹60,000 is available for 1-2 kW solar plants. Households with a consumption of 150-300 units can receive between ₹60,000 and ₹78,000 for 2-3 kW systems, while those consuming over 300 units are eligible for ₹78,000 for systems above 3 kW.
Have any queries?
Contact us today!
Common Solar On-Grid Services
Site Survey & Consultation
Assessment of rooftop or land suitability
Energy consumption analysis
ROI and feasibility report
System Design & Engineering
Custom design based on energy needs and site conditions
Electrical layout, panel placement, and inverter selection
Installation & Commissioning
Mounting of solar panels
Electrical wiring and inverter setup
Grid synchronization
Net Metering Setup
Integration of a bi-directional meter
Coordination with local electricity board for approvals
Monitoring & Maintenance
Remote performance monitoring
Periodic cleaning and inspection
Troubleshooting and repairs
Government Subsidy & Documentation
Assistance in applying for subsidies (if available)
Handling paperwork for grid permissions and incentives
Benefits of On-Grid Solar Systems
- Lower Electricity Bills: Sell excess energy back to the grid.
- No Battery Required: Reduces system cost and maintenance.
- High Efficiency: Direct power usage with grid backup.
- Government Incentives: Often eligible for subsidies and net metering benefits.
Working of an On-Grid Solar System for Home
- Solar Panels Capture Sunlight:
Photovoltaic (PV) panels convert sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity. - Inverter Converts DC to AC:
A solar inverter (grid-tied inverter) converts DC into alternating current (AC) — which is used by household appliances. - Power Your Home First:
The AC electricity powers your home’s appliances in real-time.
If your home needs more electricity than generated, it pulls the extra from the grid. - Excess Electricity Goes to the Grid:
If your solar system generates more electricity than needed, the surplus is sent back to the grid through a net meter. - Net Metering Tracks In/Out Flow:
A bi-directional (net) meter records:
1. Electricity imported from the grid
2. Electricity exported to the grid
At the end of the billing cycle, you’re billed only for the net units used (import – export).





